
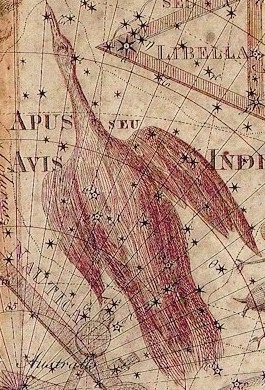
We are all aware about the fact that constellations were pictures made in the stars seen by the ancient people. Today, what we call as constellations are a group of aligned stars called asterisms. One such constellation in the sky is the ‘Bird of Paradise.’ Originally known as Apus, it is derived from the Greek word apous meaning ‘footless’. Located in the southern hemisphere, the constellation was drawn by Petrus Placinus who was a Dutch astronomer from the 16th century. He, along with the explorers Pieter Dirkzoon Keyser and Fredrick de Houtman had made various observations and named it “Paradysvogel Apis Indica” meaning the ‘Bird of Paradise’. However, it was later altered as ‘apis’ which means an ‘Indian bee’. The word apis was mistaken for the word “avis” which means ‘bird’ in Latin. This resulted in two constellations being renamed. Apis was renamed as “Musca” meaning the fly and “Avis Indica” was renamed as Apus.”
The stars in the constellation are:
- Apodis (Alpha Apodis): It is the brightest star in the Apus with a magnitude of about 3.825. With an approximate of 410 distant light years, it is classified as a K–type giant.
- Apodis (Gamma Apodis): The second brightest star in the constellation, it has a magnitude of about 3.872. It is about 160 light years distant and is a yellow G–type giant star.
- Apodis (Apodis Delta): It has two components, namely the Delta–1 and Delta–2. The Delta–1 is a brighter component. Delta Apodis is a binary star which is approximately 800 light years distant. Delta-1 is an M–type red giant star whereas the Delat–2 is an orange K–type giant star.
- Apodis (Kappa Apodis): It designates two stars namely Kappa–1 Apodis (HR5730) and Kappa–2 Apodis (HR 5782). The former is about 1020 light years distant and is a blue–white B–type sub-giant whereas the latter is a combination of a B–type blue–white giant and orange K-type.
- Apodis (Beta Apodis): Located approximately 158 light years away from the earth, it is an orange K–type giant star. With a magnitude of about 4.23, it is the third brightest star in the constellation.
- Apodis (Zeta Apodis): With an apparent magnitude of about 4.76 and approximately 312 light years distant from the earth, it is an orange K–type giant.
- Apodis (Eta Apodis): It is an A–type star and is classified as an Am star or a metallic–line star.
- Apodis (Epsilon Apodis): Approximately 551 light years away from the earth, it is a blue–white B–type main sequence star. Its brightness varies by about 0.05 magnitudes.
Johann Bayer, an astronomer named this constellation ‘Apus Indica’, meaning the ‘Bird of India’. It is also said that the name comes from a Greek word apous which means ‘feet’, which in turn, is related to a Greek myth. It is also argued that the word is derived from the Greek word apousia which means ‘absence’. In order to fill the void space in the southern hemisphere, Johann Bayer designed the constellation.
It has two deep sky objects. They are:
- NGC 6101: It can be observed through a 4.5 inch telescope as it is a small globular cluster in Apus. Apparently, it has a magnitude of about 9.2 and lies about seven degrees to the north of Gamma.
- IC 4499: The southernmost globular cluster in the sky, it is small and faint. This means it is closest to the south celestial pole and is seen as a small patch in an eight inch telescope.

Apus lies in the third quadrant of the southern hemisphere between the celestial pole constellation of Octans and triangle of stars that form the Triangulum Australe, meaning the ‘Southern triangle’ constellation. It is the 67th constellation in terms of its size and occupies an area of about 206 square degrees. It lies between latitudes +50 and -900 and is about 411 light years away from the earth.

It is believed that the Greek name apous refers to a bird swallow that did not have feet. Also, the name Apus Indica is derived from the tales spoken by the Dutch seafarers who believed that the European travellers received alive birds as gifts. The wings and feet of these birds were removed to be used as decorations and this led to a belief that these birds came from paradise and had never touched earth until their death
G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.