
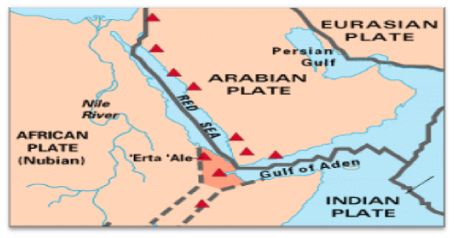
The Arabian Plate is the one that forms boundaries with 3 major plates – the Eurasian Plate, African Plate and Indian Plate. It is located in the Middle East Region of Asia; it covers approximately 6 million sq. km and its net movement is northward. It encompasses the continents of Africa and Southern Asia, along with its main water bodies of the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea. The Arabian Plate mostly consists of the Arabian Peninsula that extends the northward to Turkey.
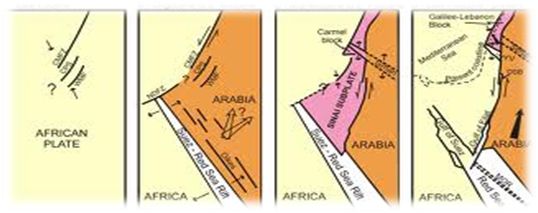
Over millions of years, the Arabian Plate has been moving northwards, colliding with the Eurasian Plate. During much of the Phanerozoic eon, the Arabian Plate was a part of the African Plate. However, the collision led to a mingling of plate pieces and mountain ranges that extended in the west from the Pyrenees, crossing the Southern Europe end and to Iran forming the Alborz and Zagros Mountains. After the separation of Africa and Arabia in the Oligocene, the Plate has been moving slowly toward the Eurasian Plate.
Covering an area of about 5,000,000 sq. km, it is located at 30°E to 75°E latitude and 10°N to 45°N longitude. The plate moves at about 4.65 cm per year in the northeast direction.
The Arabian Plate is important due to the following reasons:
- It has all the three main tectonic boundaries, namely the divergent, the convergent and the transform, the boundaries of which include the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden, Zagros-Taurus and Dead Sea respectively.
- In addition to all kinds of structures, the Arabian Plate includes a wide range and subvariety of all the three rock types, the igneous, the metamorphic and the sedimentary rocks.
- The plate incorporates most of the world’s oil reserve.
The Pakistani fishers have noticed a mud volcano in the Arabian Sea. According to NASA, the mud volcanoes are formed underwater when the layers of silt or clay become pressurized either by a build up of hydrocarbon gases or by a tectonic activity. The sediments that form Pakistan’s coastal plains and an offshore slope is been subducted by the Arabian Plate under the Eurasian landmass.
G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.