
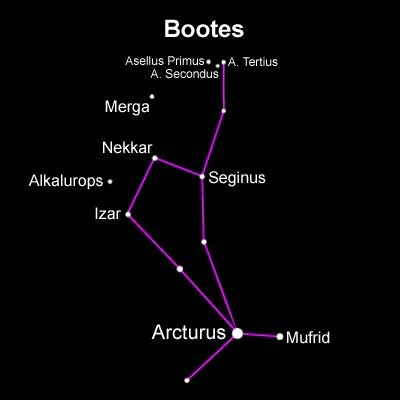
There are many known and heard constellaions in the sky. Some are visible and easily recognized while few others does exist but are not well known. One such constellation is Bootes. The correct pronunciation is “bou’outus”, each ‘o’ is pronounced separately while stressing on the second syllable. So, the correct pronunciation is ‘Bo–-OH–teez’. Bootes may be the oldest known constellation but comparatively is not widely known. It is a constellation in the northern hemisphere and is referred to as ‘the Herdsman’ as it is often visualized as a herdsman holding a staff and two dogs in a leash which is chasing Ursa Major around the poles. The Greek astronomer Ptolemy first documented it in the 2nd century and named it Bootes based on the mythological stories associated with it.
Bootes has numerous stars, out of which, there are five stars with known planets. Some of its major stars are:
- Arcturus (Alpha Bootis): It is the third brightest star in the northern hemisphere and the night sky. Its apparent magnitude is about -0.04. However, it is the third individual brightest star after Alpha Centauri A in the night sky.
- Nekkar (Beta Bootis): It is a giant yellow G–type giant flare star that increases its luminosity dramatically for a few minutes. It derives its name from the name Nekkar which is a mis–transliteration of an Arabic word that meant ‘cattle driver’.
- Seginus (Gamma Bootis): It varies in brightness due to radial and non–radial pulsations on its surface and is a Delta Scuti type variable star. It is approximately 85 light years distant from the earth. It is luminous between the magnitudes 3.02 and 3.07 respectively.
- Izar (Epsilon Bootis): It is a binary star consisting of a bright orange giant and fainter main sequence. It is approximately 300 light years away and is also, sometimes known as ‘Pulcherrima’ which means ‘the loveliest’.
- Muphird (Eta Bootis): Muphird is a spectroscopic binary star that has a period of 494 days. Also known as Saak, it derives its traditional name from an Arabic phrase ‘the single one of the lancer’. It is located about 37 light years from the earth and contains elements that are in excess and heavier than hydrogen.
- Alkalurops or Mu Bootis: It is derived from a Greek word meaning “the shepherd’s staff.” It is a triple star and is approximately 121 light years distant from the earth. An F–type giant, it has an apparent magnitude of about 4.31.
- Merga (38 Bootis): It comes from an Arabic phrase meaning ‘the chained woman’. The star has an apparent magnitude of about 5.74 and is about 153 light years away from the earth.
- Psi Bootis or Nadlat: It is an orange K–type giant star and is about 250 light years distant along with an apparent magnitude of 4.52.
- Tau Bootis: It is another binary star consisting of a yellow–white dwarf and a dim red dwarf. Although it was discovered in 1996, it got confirmed in 1999. It is approximately 51 light years from earth.
The Greeks named it Bootis or Nekkar meaning ‘cattle driver’. It was also called the constellation Arctophylax meaning ‘bear watcher’ or bear keeper.” Due to various myths associated with it, it is referred by different names.
It does not have any deep objects but a void known as the Bootes void or the Great void or the Super void. It lies in the spherical shape of the region in the sky and contains quite a few galaxies; The Bootes Dwarf Galaxy is located approximately 197,000 light years away from the earth and is one of the faintest galaxies known. It has an absolute magnitude of about 13.1 and was discovered in 2006 and on the other hand, the NGC 5466 is a globular cluster and about 52,800 light years from earth. Discovered in 2006, it is notable because it contains a blue horizontal branch of stars and its metal is as poor as regular globular clusters. It also has three meteor showers namely the January Bootids, the June Bootids and the Quadrantids.
Bootes is located in the third quadrant of the northern hemisphere, between latitudes +90° and -50°. It is about 219 light years away from the earth and is clearly visible in spring through the summer.
This constellation occupies 907 square degrees of space in the sky, making it the 13th largest constellation of the night sky.
Bootes neighbours constellations such as Canes Venatici, Coma Berenices, Corona Borealis, Draco Hercules, Serpens Caput, Virgo and Ursa Major.
The Greeks imagined or visualized this constellation as a herdsman holding a staff and two dogs on a leash chasing Ursa Major. However, according to another myth, this constellation is visualized as a ploughman driving the oxen, tied to the polar axis in the Ursa Major constellation. The two dogs are said to belong to the Canes Venatici constellation. It is also said that this constellation kept the skies turning. Another Greek myth states that Bootes is identified as Icarius, a grape grower and a wine–maker. God Dionysus had taught him to make wine which when he did make got him killed. After tasting Icarius wine, his friends were high; as they were tasting wine for the first time, they mistook drunkenness to the effects of poison. Assuming that Icarius wished to kill them by poisoning them, they murdered Icarius. His body was found by his dog Maera who ran and brought Icarius’ daughter Erigone to his body. On seeing the dead body of her father, she hanged herself to death while the dog jumped off a cliff. Seeing this Zeus thought that they deserved a place in heaven; he transformed them into constellations: Icarius became the Bootes, Erigone into Virgo constellation and the dog became the Canis Major.

G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.