
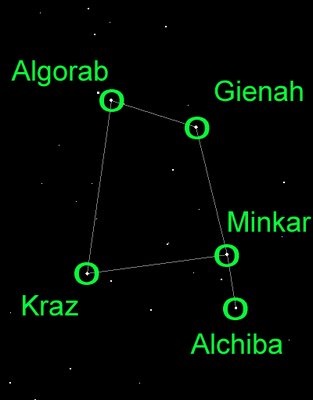
An easy constellation to pick out in the sky and a friendly sight in the heavens is the constellation Corvus. It is a small constellation in the southern hemisphere and one of the 48 constellations created by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the 2nd century. In Latin, Corvus means ‘raven or crow’. It is a small, box–like asterism and has no bright star and consists of 11 stars which are visible to the unaided eye. A constellation of the Hercules family group, it is best visible in the month of May at 9 pm. Let us discuss about this further.
Some notable stars of this Constellation are:
- The SAIL (SPICA’S SPANKER): Delta, Gamma, Epsilon and Beta Corvi are the four brightest stars of this Constellation that form an asterism known as the Sail or Spica’s Spanker.
- Gienah (Gamma Corvi): It is basically the brightest star in Corvus constellation with a magnitude of about 2.59 and is about 165 light years away. It is believed to be a binary star.
- Kraz (Beta Corvi): Kraz is basically a yellow–white bright giant, about 140 light years away from the earth. The visual magnitude of Kraz varies between 2.60 and 2.66. It is also the second brightest star in Corvus. Kraz is about 160 times brighter than the sun.
- Algorab (Delta Corvi): Delta Corvi is about 87 light years away from the solar system and has a visual magnitude of 3.1. Its traditional name originates from the Arabic word al–ghuraab which means ‘the crow’.
- Minkar (Epsilon Corvi): It has a visual magnitude of 3.02 and is about 303 light years away. Its traditional name, ‘Minkar’ is originated from the Arabic word almanxar which means ‘the nostril of the crow’.
- Alchiba (Alpha Corvi): Alchiba is the fifth brightest star in the constellation with a visual magnitude of 4.02. It is also four times brighter than the sun. Its traditional name is originated from the Arabic word al hibaa which means ‘tent’. It is also been suspected to be a binary star.
- n Corvi (Eta Corvi): Eta Corvi is the sixth brightest star in this constellation. It is a main sequence star with a visual magnitude of about 4.31 and is about 59.4 light years away. It is slight massive, but younger than the sun.
- VV Corvi: In Corvus, VV Corvi is basically a double star comprising of two stars which orbit each other with a period of 1.46 days. They are about 289 light years away.
Some of the deep sky objects in the constellation include:
- Antennae Galaxies (NGC 4038/ NGC 4039, Caldwell 60/61): They are basically a renowned pair of interacting galaxies in the Corvus constellation. They are also sometimes referred to as Ring Tail. The Antennae Galaxies belong to NGC 4038 group, a group which comprises of between 13 and 27 members located in Crater and Corvus constellations. They have a visual magnitude of 11.2/11.1 and are about 45 million light years away from the earth.
- NGC 4027 (Arp 22): NGC 4027 is basically a barred spiral galaxy in Corvus. It is also a member of the NGC 4028 group of galaxies. NGC 4027 has a visual magnitude of 11.7 and is around 83 million light years away from the solar system. It is located less than a degree to the southwest of the Antennae Galaxies.
- NGC 4361: It is basically a large planetary nebula in the centre of the constellation. Its shape resembles a dim elliptical galaxy. It is about 50’ in diameter.
Corvus lies in the third quadrant of the southern hemisphere and can be seen at latitudes between +60° and -90°.
It occupies an area of 184 square degrees, making it the 70th Constellation in size.
According to the Greek mythology, Corvus is represented as the raven (crow), Apollo’s sacred bird that originally had white feathers. The bird was told to watch over Coronis, one of Apollo’s lovers who was pregnant at that time. However, with time, Coronis fell in love with a mortal man named Ischys. Raven reported the affair to Apollo who was so enraged that he flung a curse on the bird, scorching its feathers. When Apollo sent his sister to Artemis to kill Coronis, the unborn child, Asclepius, was cut out of her womb and was given to the centaur Chiron to be raised. This child, Asclepius is represented by the constellation Ophiuchus, the serpent bearer and grew up to be a famous healer.
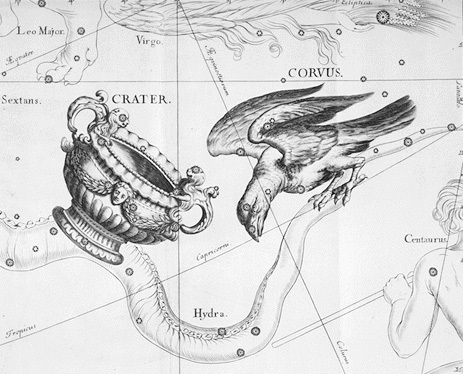
Corvus is surrounded by constellations such as Crater, Hydra and Virgo.
G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.