
The use of Cymbals in a musical ensemble justifies the expression of high strung emotions accompanied by drama and tension in a composition. The word Cymbal is derived from the Latin word cymbalum meaning ‘a small bowl’. Cymbals belong to the family of percussion instruments with an indefinite pitch. The high pitch of the Cymbal is used to accentuate the effect of compositions where the unique sound of the Cymbals can be heard above all the other instruments particularly in the romantic period orchestra. The instrument is differentiated by its distinct sound and definite rhythm where sounds are produced by clashing of the two plates against each other. In India, they are known as Manjira (small in size) and are often used in religious rituals and songs. Described as thin, round, concave metal plates, Cymbals are the only instruments to be played in pairs and the techniques involves single stroke, rotating both plates against each other and the rolls.
Images of Cymbals can be found in the 15th century miniatures of the medieval ages. The middle age saw the advent of Cymbals in Europe, introduced by the Saracens who brought them from Spain and Italy. Turkey has been well known for its expertise in Cymbal manufacture from the 17th century. The Turkish Cymbals began to be scored in the orchestras. The best known use of Cymbals is probably from Mozart’s Turkish opera of 1782. Finally established in the later part of the 19th century, Cymbals are believed to have originated in Asia and are amongst the world’s oldest percussion instruments. They were introduced to Europe in the middle ages.

Sound is produced when one Cymbal is struck against the other. The Cymbals act as both a vibration–generator and resonator. The vibrations cause the sound. Maximum sound is produced near the rims of the plates. A struck Cymbal produces inharmonic partials of metal sound, which is harsh if the oscillation frequency is high. The duration of the vibration depends greatly upon the alloy, the thickness and size of the plate. Bigger the Cymbal, lower is the pitch. It is necessary that the plates are struck by overlapping and the touch is brief. This is also to ensure that there is no air pocket. Air pocket makes the sound dull and flat.

The Cymbals are made of two metal plates of various alloys and a leather straddle to hold them together. However, the component may vary with the types of Cymbals. A Hi–hat or suspended type of Cymbal may include a stick and supporting accessories.
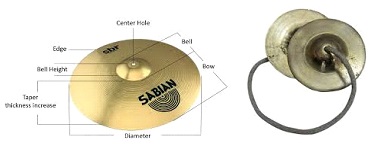
Cymbals are made from brass wire, sheet brass, nickel, silver or bronze alloys. The best made Turkish Cymbals use a combination of metals in a proportion not known. Modern Cymbals are a pair of round, slightly conical plates with a raised dome at the centre. The rim of the plates is smooth. There is a small aperture in the dome through which a leather strap is attached. For tone quality, Cymbals are made thicker at the centre. The plate is hammered with special hammers with great care and skill to produce the best possible tone. Hammering also gives the Cymbals a typical dented appearance.

Cymbals are used as an accompaniment to the other instruments in most of the orchestral performances. Sometimes, it is played with the bass drum. Legendary composers such as Mozart and Beethoven have used Cymbals in their well known compositions. Generally, different types of Cymbals are used in orchestra, percussion ensemble, jazz bands, heavy metal bands and marching groups. Drum kits usually incorporate at least one type of Cymbal, namely the Hi–hat. The smaller version of Cymbals used in India are called ‘manjira’ and are also used in singing of devotional songs.

Listed below are some of the types of Cymbals:
- A pair of Cymbals is used to stress upon important musical accents or can be used as quiet rhythm instruments in the background.
- Suspended Cymbals can accomplish a wide variety of tasks using sticks and greater dynamic flexibility but cannot match the effects created by the pair of Cymbals.
- The Hi–hat Cymbals are rarely used in the modern orchestra literature, but has been an integral part of dance music of all kinds of jazz, rock and pop from the early 20th century and was known as Charleston Machine.
- Finger Cymbals are a smaller version of the pair of Cymbals and because of their low dynamic level, they are rarely used in orchestra. Their construction follows that of a pair and they loosely belong to the Cymbal family.
- Bell Cymbals are a type of Splash Cymbals and possess very little tapering. When struck with a drumstick, it gives a very high–pitched distinct sound.
- China–type Cymbals are also known as ‘trash cymbals’ as they are manufactured to produce sound that is explosive and has a trashy tone. In western music, they are referred to as ‘china type’.
- Clash Cymbals are also referred to as hand or suspended Cymbals and are usually struck with the hands. In western music, they are played with a drumstick.
- Crash Cymbals are used in orchestras and bands and are used to produce a ‘crash sound’. They have a thin edge, which is used in light rock while the thicker ones are used to create loud accent in rock music.
- Manjira or Taal Cymbals are small in size and are very popular in India. They are used in singing or performing devotional music.
Other variant of Cymbals include Sizzle, Swish, Splash, Crash Ride and Flat–ride Cymbals.

Solo pair of Cymbals was played to a great effect by Nicolaus Huber. Legendary composers such as Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Ludwig Van Beethoven, Piotr Tchaikovsky and Franz Liszt used the orchestral pair of Cymbals in their great compositions.
G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.