
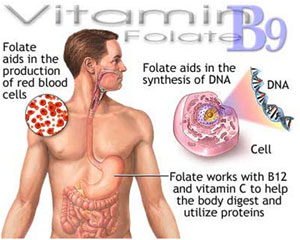
We have all heard about DNA in our body. What aids in its synthesis? Why is it important? The very first name that comes to our mind when we talk about DNA is Folic Acid or Folacin or Folate as its known when it is biologically active. Folic Acid is useful for the body during pregnancy and infancy. The DNA that it produces is required for rapid cell division and organ/tissue formation in the developing baby.
What is the role of Folate in the body?
Folate, also known as Folacin or Vitamin B9, is a water soluble B vitamin and is naturally present in foods. Folic Acid is an oxidized form of vitamin which is used in the dietary supplements. Its main function is to act as a coenzyme or co-substrate in the synthesis of nucleic acids and in the metabolism of amino acids. Folate plays an important role in the body of women as it makes new cells and maintains it. It prevents about 75% of the defects at birth of the spine and brain.
What is the difference between Folate and Folic Acid?
Both Folate and Folic Acid are forms of B vitamin. Folate is naturally found in foods whereas Folic Acid is found in vitamin supplements. Folic Acid is used to enrich and fortify some processed foods and is a synthetic form of Folate.
How much of Folate is enough for the body?
On an average, infants should consume about 65 micrograms, children should consume about 150-200 mcg in a day, teens should have an adequate intake of about 300 mcg and adults should consume about400 mcg of Folate, daily. However pregnant women require an increased amount of consumption which is about 500 mcg per day.
How does lack of Folate affect you?
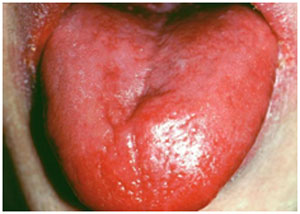
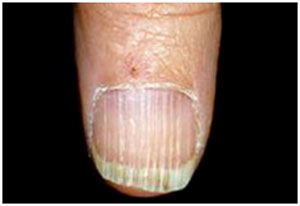
Deficiency of Folate is rare. It can be due to a combination associated with poor diet, alcoholism and mal-absorptive disorders. Deficiency of Folate leads to fatigue, poor growth, soreness and shallow ulcers in the tongue. It may also result in the changes in the skin, hair or fingernail pigmentation and elevated blood concentrations.
What are the natural sources of Folate?
The good and natural sources of Folate are dried beans, peas, lentils, spinach, beets, broccoli, corn, peas, tomatoes, orange juice, and banana along with enriched grain products like pasta, cereals and bread. Whole grain cereals are also good sources of Folate. Peanut, butter and sunflower seeds are rich sources of Folate.

What are the diseases that are caused due to lack of Folate?
The diseases are:
- Cancer: Lack of Folate increases the risk of colorectal, lung, pancreatic, oesophageal, stomach, cervical, ovarian, breast and other cancers. This is so because it influences the role of carbon metabolism and subsequently affects the DNA replication.
- Cardiovascular disease and stroke: Folate lowers the levels of homocysteine and is involved in metabolism. However lack of desired Folate leads to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Megaloblastic Anaemia: It is caused when the red blood cells are incompletely formed in the body. This leads to immature cell growth and the red blood cells may not function like the healthy ones and causes Anaemia.
- Neural Tube Defects: It is a disease associated with the brain, spine or spinal cord. Its two types are spina bifida and anencephaly. It occurs during the first month of pregnancy and people who are obese and diabetic are more prone.
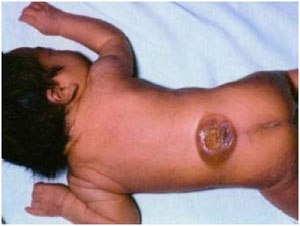
Neural Tube defects
Add/View Comment
G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.