
Would we humans have existed without procreation? Every individual organism in the universe is basically the result of procreation or reproduction. Procreation or reproduction is a biological process through which new individual organisms are produced by the involvement of two individuals of the opposite sex. Each of the two parent organisms contribute for the procreation of a new organism. Procreation is a fundamental feature of life and each individual organism in this universe exists because of reproduction. The reproduction process is carried with the help of our genitals or sex organs. Men and Women have different sex organs. The reproductive anatomy includes both the genitals that are visible outside the body as well as the internal sex and reproductive organs.
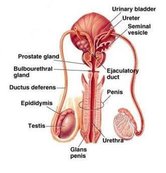
The external structures of the male reproductive system include the penis, scrotum and the testicles.
The internal organs of the male reproductive system include epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra, seminal vesicles, prostate gland and the bulbourethral glands.
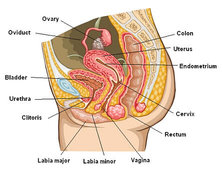
The external structures of the female reproductive system include labia majora, labia minora, bartholin’s glands and the clitoris.
The internal organs of the female reproductive system include vagina, uterus, ovaries and the fallopian tubes.
The function of the male reproductive system is to transport and maintain sperm and the protective fluid (semen). Sperms are the male reproductive cells.
The male reproductive system also acts during sex to discharge the sperms within the female reproductive tract.
They also produce and secrete male sex hormones (testosterones), which are mainly responsible in maintaining the male reproductive system.
The female reproductive system carries out several different functions:
-
For reproduction, it produces the necessary female egg cells, also known as ova.
-
The female reproductive system is also designed to menstruate.
-
It also produces the female sex hormones (estrogens) that are mainly responsible in maintaining the reproductive cycle.
-
Penis: It is a male organ that is used during sexual intercourse. Penis has three parts: the root, which attaches to the wall of the abdomen; the body or shaft and the glans, which are the cone-shaped part situated at the end of the penis. The glans, also referred as the head of the penis, is covered with a lose layer of skin known as foreskin. The opening of the urethra, which is at the tip of the penis, is a tube that transports the urine and the semen. The body of the penis being cylindrical in shape consists of three circular shaped chambers. These chambers are made up of special, sponge like tissue which contains large spaces that fill with blood when a man is sexually aroused. When the penis is filled with blood, it becomes erect and rigid, which allows for penetration during intercourse. When the man reaches sexual climax the semen, which contains sperm is expelled through the end of the penis. And when the penis is erect the flow of the urine is blocked from the urethra, allowing only the semen to be ejaculated.
-
Scrotum: It is a loose pouch of skin that hangs behind and below the penis. The scrotum contains the testicles and many nerves and blood vessels. For the testicles, the scrotum acts as a “climate control system”. The testicles must be at a slightly cooler temperature than our body for the normal sperm development. The special muscles situated in the wall of the scrotum allow it to contract and relax. It moves the testicles close to the body for warmth and farther away from the body to cool off the temperature.
-
Testicles (testes): The testicles are oval organs that are situated in the scrotum. They are secured at both the ends by a structure known as the spermatic cord. The testicles are mainly responsible for making male sex hormones (testosterones) and for generating sperm. Situated within the testes are coiled masses of tubes known as seminiferous tubules, which are mainly responsible for producing sperm cells.
-
Labia majora: The labia majora also known as the outer lips protect and enclose the other external organs. They are large, fleshy and are comparable to the scrotum in the males. The labia majora or the outer lips contain the oil-secreting glands and the sweat. They are usually covered with hair after puberty.
-
Labia minora: The labia minora also known as the inner lips are small as they just lie inside the labia majora and surround the openings of the vagina.
-
Bartholin’s glands: The bartholin’s glands are situated just besides the vaginal opening and they produce a fluid known as mucus.
-
Clitoris: The two labia major and minora meet at the clitoris, which is basically a small, sensitive protrusion. It is covered by a fold of skin known as the prepuce. The clitoris is very sensitive to stimulation.
The internal organs are also known as the accessory organs.
-
Epididymis: The epididymis is a long, coiled tube that is situated on the backside of each testicle. Its main function is to transport and store sperm cells that are produced in the testes. The epididymis is also responsible for bringing the sperm to maturity as the sperms that emerge from the testes are immature and incapable of fertilization. When a man is sexually aroused, the contractions force the sperm into the vas deferens.
-
Vas deferens: The vas deferens is a long, muscular tube that basically travels from the epididymis into the pelvic cavity, to the backside of the bladder. The function of vas deferens is to transport the mature sperm to the urethra, which is a tube that carries urine or sperm to the outside of the body.
-
Ejaculatory ducts:The ejaculatory ducts are formed by the fusion of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicles. The ducts usually empty into the urethra.
-
Urethra: It is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. In males, the urethra has an additional function that is ejaculating semen at orgasm and blocking the flow of urine.
-
Seminal vesicles: The seminal vesicles are sacs, which are similar to pouches that are attached to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder. They produce a rich fluid (fructose) that provides the sperm with a source of energy to move. The fluid of these seminal vesicles makes up most of the volume of a man’s ejaculatory fluid.
-
Prostate gland: The prostate gland is a walnut sized structure that is situated below the urinary bladder in front of the rectum. It contributes additional fluid to ejaculate and also helps to nourish the sperms. The urethra, which carries the ejaculation, runs through the centre of the prostate gland.
-
Bulbourethral glands: The bulbourethral glands or also referred as the Cowper’s glands are pea-sized structures that situated on the sides of the urethra, below the prostate gland. They produce a clear and slippery fluid that directly empties into the urethra. The produced fluid serves as lubricant to the urethra and to neutralize any acidity that may be present due to the drops of urine in the urethra.
Vagina: The vagina is a canal that joins the lower part of the uterus also known as the cervix, to the outside of the body. The vagina is also referred as the birth canal.
Uterus (womb): Uterus, the hollow and pear-shaped organ is home to developing fetus. The uterus is divided into two parts: the main body of the uterus, known as the corpus and the cervix, the lower part that opens into the vagina. To hold a developing baby the corpus can easily expand. There is also a channel through the cervix that helps the menstrual blood to exit and the sperms to enter.
Ovaries: The small oval-shaped glands located on either side of the uterus are known as the ovaries. The main function of the ovaries is to produce eggs and hormones.
Fallopian tubes: The Fallopian tubes are narrow tubes that are attached to the upper part of the uterus and they serve as a tunnel for the egg cells (ova) to travel from the ovaries to the uterus.
G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.