
Potassium, also symbolised as ‘K’, is derived from the Latin word ‘Kalium’which means ‘alkali’. It is a soft and silvery metal that can be easily cut through knife. A powerful element in improving the health, Potassium is the third most abundant mineral in the human body and is the seventh most abundant metal of the earth’s crust. Potassium is highly reactive and hence it is not found free in nature. It is either dissolved in seawater or in the ionic salts.
The mineral Potassium regulates along with Sodium to balance the fluids in the body. It is necessary in the human body as it promotes the regular heartbeat, helps build and contract muscles, regulates blood pressure and controls water balance in the body tissues and cells. Potassium preserves the cell functions and affects the fluid balance in the body. Also it regulates the actions of the kidneys by filtering the blood and helps in the movement of the fluids, both in and out of the cells. Potassium is also needed by the body for various enzymatic and metabolic pathways.

A healthy diet does not require any other intake of Potassium supplement in the body. The average Potassium intake for infants should be 780 mg, for children should be 1600 mg and among adults it is 3500 mg. The daily recommended allowance of Potassium intake among both males and females should be 4.7 grams. However this must also work in harmony with the proportion of Sodium and Magnesium in the blood.
Potassium is a mineral which is very important and critical for the functioning of the nerve and muscle cells. Low Potassium means when there is a lower than normal level of Potassium in your bloodstream. The normal Potassium level in the body is about 3.6 to 5.2 mmol/L. Low Potassium level, which is about less than 2.5 mmol/L proves dangerous and threatens life. The common cause that may lead to low Potassium in the body is excessive loss of Potassium in urine.
Some conditions and Illnesses caused due to low Potassium are:
- Chronic Kidney failure: There is a gradual loss of kidney function. The filtered fluids from the blood are excreted in the urine. The symptoms of kidney failure include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, changes in the output of the urine, decreased mental sharpness, muscle twitches and cramps, hiccups, swelling of the feet, high blood pressure, etc.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: This is a serious complication of diabetes where the body produces high levels of blood acids, called ketones and is unable to produce enough insulin. The symptoms that can be noticed are excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, fruity-scented breath, etc.
- Diarrhoea: It is a loose watery stool that occurs frequently. Its common symptoms are abdominal cramps, fever, blood in the stool, bloating, etc.
- Excessive sweating
- Excessive use of laxatives
- Vomiting
- Primary aldosteronism: It is a hormonal disorder leading to high blood pressure. One of the hormones that our body produces is aldosterone, which helps in balancing the sodium and potassium in the blood. In this disorder, the adrenal glands produce too much aldosterone which causes you to lose Potassium and retain sodium in the body.
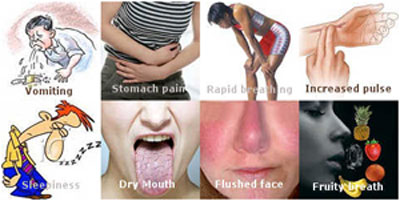
The medical term for the high Potassium in the body is called Hyperkalemia. In a normal human body, the proportion of Potassium, should not exceed more than 7.0 mmol/L. Its common causes include adrenal failure, heavy drug intake or alcohol consumption, red blood cells get destroyed due to severe injury or burns, excessive use of Potassium supplements, etc.
After calcium and phosphorous, Potassium is an important mineral of the body. A proper diet should be practised in order to maintain a balanced proportion of Potassium in the body. These include:
- Fruits: Bananas, dried apricots, watermelon, fresh dried figs, nectarine, oranges, papayas, prunes, raisins, etc.
- Vegetables: Avocado, artichoke, Brussels sprouts, cooked dried peas, potatoes, pumpkin, spinach, tomato, winter squash, etc.
- Dairy products: It includes buttermilk, milk and yogurt.
- Meat and other alternatives: Fish, sardines, clams, dried peas and tofu.
- Drinks: It involves milk, orange juice, prune juice, tomato juice and vegetable juice.

G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.