
Have you ever imagined what brings taste to the food that you eat? What is it that lubricates the food and makes it easy to swallow? Which system is responsible for the food to be swallowed and eventually get digested? What manipulates the tongue and lips to make sounds and speeches? It is the saliva. It is when we taste, smell or eat food, the quantity of the saliva increases whereas when we are asleep, the quantity decreases.
Saliva is a thick, colourless and glistening liquid with about 98 percent water in our mouth. It appears glistening because of the mucus, a slippery secretion and this mucus helps the saliva with a thick texture than pure water. It is from the blood that the water in the saliva is obtained. This water allows the saliva to become a part of the capillaries in the Salivary Glands. The saliva, in addition to water, contains chemicals like the mucus, salts, antibacterial substances and enzymes. It prevents the tooth decay as it contains the bacterial cells that kill the bacteria. Also, the digestion of starch into a sugar called the maltose is done because of an enzyme, salivary amylase that the saliva contains.
Salivary Glands are exocrine glands that produce saliva. They are generally glands with ducts that secrete amylase, which is an enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose. On an average, the Salivary Glands make about 1-2 litres of liquid a day, which can be approximately 10,000 gallons of saliva in a lifetime. Internally, the Salivary Glands are divided into lobules. The blood vessels and the nerves branch out into the lobules and enter the glands at the hilum. The lobules are:
-
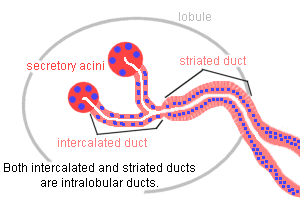
Acini: They are the secretory cells, found in a group and are connected to the ductal system. Each acinus is located at the terminal part of the gland. It is classified into three forms, namely, serous, mucoserous and the mucous.
-
Ducts: A duct is a circumscribed channel between the exocrine gland to the organ. In this system, the intercalated ducts, a portion of an exocrine gland that leads directly from the acinus to a striated duct, forms the lumina and this in turn, joins with the striated duct that connects an intercalated duct to an interbolar duct.
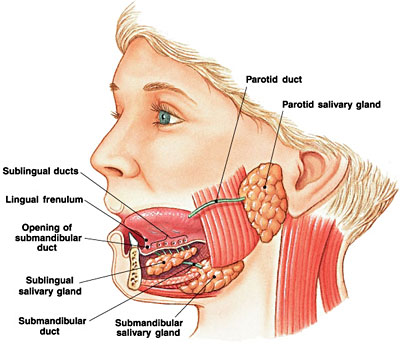
Salivary Glands are located in and around the mouth and throat. They secrete the saliva near the upper teeth with the help of the salivary ducts, parotid through the tubes that drain saliva; through the tongue is the submandibular and sublingual through many ducts in the floor of the mouth.
The important and primary function of the Salivary Glands is to secrete saliva. The saliva, with the help of the Salivary Glands, performs the following functions:
-
Moisten the dry foods in order to aid comfortable swallowing.
-
Act as a medium for the suspended food materials that stimulate the taste buds chemically.
-
Digestion of the carbohydrates and starch.
-
The contents of the oral cavity are buffered with its high concentration of bicarbonate ion.
-
Kill the bacteria that cause the infections or disorders.
-
Act as a source of calcium and phosphate.
-
The secretory products are moved towards the excretory duct by contraction.
The Salivary Glands produce a thick liquid released into the mouth, which lubricates the mouth and begins the breakdown of the food that is chewed and is made of water, enzymes, mucin and protein. These glands are classified into three major glands and other minor glands:
-
The Parotid Gland: The Parotid Gland is situated below the ear and is the largest Salivary Gland. The parotid releases the saliva through an opening and enters the inside of the cheek beside the upper molar teeth, one on each side.
-
The Submandibular Gland: Located under the mandible, that is, the lower jawbone, it releases the saliva under the front tongue, behind the front teeth. Again, it is one on each side.
-
The Sublingual Gland: It releases the saliva from the small openings under the tongue and hence, is situated under the tongue. They are the pair of the Salivary Glands that sit next to each other under the tongue. It is categorised as mixed glands.
-
Minor Salivary Glands: There are about 800 to 1000 minor Salivary Glands that are located in the floor of the mouth or between the muscle fibres of the tongue. About 1mm to 2mm in size, they are surrounded by the connective tissues but not enclosed by it.
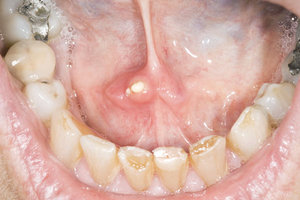
The common disorders include:
-
Sialolithiasis: Also known as the Salivary Gland Stones, they are tiny and calcium-rich stones inside the glands that cause dehydration, decreased food intake, etc. The gland’s duct is blocked by the stone and is painful and swollen.
-
Sialadenitis: It is an infection that is caused due to the accumulation of bacteria in the mouth. It is painful and hence, without proper treatment, the severity increases.
-
Viral Infections: Viral infections, like mumps, affect the salivary glands. However, this causes facial swelling, pain and difficulty in eating.
-
Cysts: Cysts are tiny, fluid-filled sacs and are often found in babies who have problem of ear-development before birth. These may result in traumatic injuries, infections or Salivary Glands or tumours.
-
Benign Tumours: A non-cancerous tumour, Benign Tumours occurs in the parotid gland. It grows slowly and appears to be a painless lump at the back of the jaw, below the earlobe.
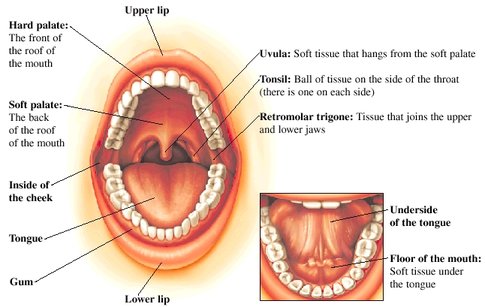
All the Salivary Glands release saliva in the mouth and the throat. A dry mouth may result into many disorders. Common symptoms of which include an abnormal or foul taste, decreased ability in opening the mouth, fever, facial pain, redness on the side of the face, swelling of the face, etc.
G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.