There are several activities (physical tasks) that we do the entire day. These include walking, running, sitting, sleeping, drinking, eating, washing, etc. All these actions are governed by the ‘motors’ of the body. These motors are also considered as the brakes or the shock absorbers of the body. They are the ‘Skeletal Muscles’. The Skeletal Muscles not only indicate strength but also help in maintaining posture and act as a store of protein. The muscular system forms the most important part of the human body. They are classified into three types namely, skeletal, smooth and cardiac.
Skeletal Muscles, as the name suggests, are the muscles that move and support the skeleton. Out of the three types of muscles in the muscular system, that is, skeletal, smooth and cardiac, the Skeletal Muscles alone constitute to about 50 percent of the body weight. There are 640 Skeletal Muscles in an individual. It is the Skeletal Muscle that acts as a link between the two bones at their joint. The muscles are arranged in such a manner that when they contract or expand, the bones move in layers. The bones that are nearest to the skin are the superficial muscles and the ones closest to the inside of the body are the deep muscles. Hence, Skeletal Muscles are voluntary muscles that can be consciously controlled.
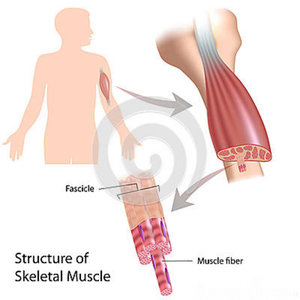
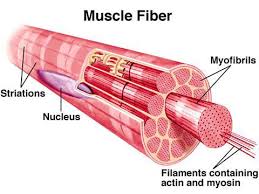
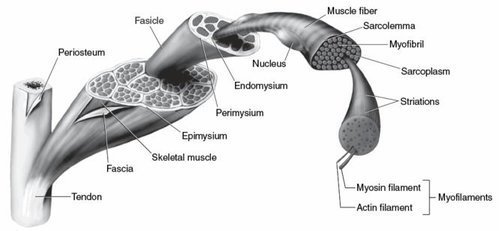
Skeletal Muscles are voluntarily under the control of the somatic nervous system. They are a form of striated muscle and are attached to the bones by bundles of collagen fibres that are known as tendons. Skeletal Muscles are composed of individual components ‘myocytes’ also called ‘muscle fibres’. These muscle fibres are formed by the fusion of myoblasts, a muscle cell, and are long, cylindrical and multinucleated cells that are called myofibres. They are then composed of myofibrils made of actin and myosin filaments and are responsible for the appearance that is vital for the muscle contraction. They are held together by a connective tissue.
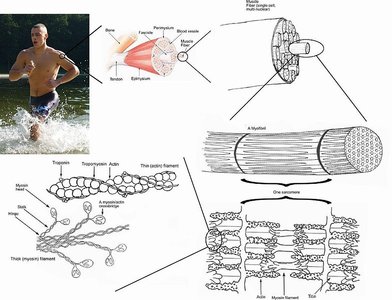
The structure of the skeletal muscle depends on the colour of the muscle fibres which also reflects the content of myoglobin in them. They are categorised as:
-
Red Fibres: These are red as they indicate high levels of myoglobin and oxygen storing proteins.
-
White Fibres: The low content of myoglobin appears white.
-
Fast Twitch: A Fast Switch is the one in which the myosin can split the ATP quickly.
-
Slow Twitch: On the contrary, the Slow Twitch generates the ATP by a long-term system of energy transfer. In a muscle fibre, every macromolecule is arranged in order to ensure that the function is met. The myofibrils are located in the sarcoplasm, which is a plasma membrane with the cytoplasm. There are mitochondria situated between the myofibrils. It is because of the sarcoplasmic reticulum that the myofibrils hold the calcium ions that are necessary to cause muscle contraction.
There are four different types of Skeletal Muscles depending on the different patterns of the arrangement produced by the fascicles. They are as follows:
-
Parallel Muscles: The fascicles run parallel to the direction of the muscle and work on a whole function that is similar to the single muscle fibre. Most of the muscles in the body are parallel ones and are seen in variety of shapes like flat bands, spindle shaped, and also large protrusions known as the belly.
-
Convergent Muscles: As they cover a broad surface, the fibres allow a versatile movement. They do not pull the muscles in the same direction or in the opposite one.
-
Pennate Muscles: An oblique angle is formed to the tendons through the body with the fascicles. As they pull the tendons at an angle, they do not move as far as the parallel muscle. Because they possess a greater amount of muscle fibres, they generate greater tension.
-
Sphincter Muscles: The fibres of these muscles are arranged around an opening. The opening gets smaller as the muscle contracts and hence is found at the entrance and the exit of the external and internal passageways.
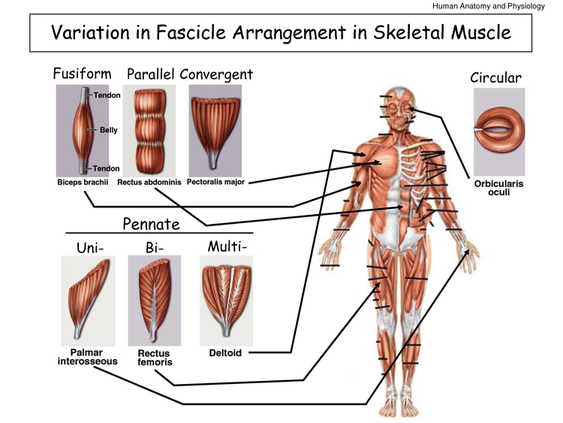
Skeletal Muscles are the striated and voluntary muscles that support the skeleton of the body. Its types include the following:
-
Skeletal Muscles of the Arm: They are the coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, brachialis anticus, triceps brachii, anconeus, pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmris lomngus, etc.
-
Skeletal Muscle of the Chest: These include the external intercostals, internal intercostals, innermost intercostals, subcostales, levatores costarum, etc.
-
Skeletal Muscle of the Hand: These consist of opponens pollicis, flexor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis brevis, adductor pollicis, Palmaris brevis, etc.
-
Skeletal Muscle of the Larynx: The Skeletal Muscles of the larynx include the cricothyroid, posterior cricoarytenoid muscles, arytenoids and thyroarytenoid.
-
Skeletal Muscles of the Leg: They consist of tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, fibularis tertius, gastrocnemius, soleus, etc.
-
Skeletal Muscles of the neck: They involve platysma, digastrics, stylohyoid, mylohyoid, geniohyoid, omohyoid, longus colli, etc.
-
Skeletal Muscle of the Scalp and Eyes: They are occipitofrontalis, corrugator supercilii, depressor supercilii, superior tarsal, superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, lateral rectus superior oblique, etc.
-
Skeletal Muscles of the Thigh: It include Sartorius, quadriceps femoris, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, vastus medialis, biceps femoris, etc.
-
Skeletal Muscle of the Vertebral Column: They are trapezius, rhomboid major, rhomboid minor, levator scapulae, etc.
There are four important characteristics that allow the Skeletal Muscles to function. They are excitability, contractibility, elasticity and extensibility. Based on these features, there are three important functions of the skeletal muscle:
-
Movement: The nervous electrical impulse is referred to the excitability and the contractility of the skeletal muscle. The nerve cell carries an electrical impulse to the muscle cell and is then translated into a chemical signal and travels to a specified muscle cell. The muscle cell receives the signal and accordingly it contracts or shortens. However after contracting or lengthening, the skeletal muscle returns to its original shape.
-
Stabilization: The Skeletal Muscles provide the stabilization of the joints. It is the ligaments that attach the bones to connect the joint. The most important stabilizers are the tendons as they connect the bone to the muscles and are held tight by the muscles.
-
Body Heat: Most of the muscles in the body are the Skeletal Muscles and hence they are very important in maintaining the body temperature. The functions of the enzymes and the metabolism depend highly on the body temperature.
As the Skeletal Muscles are necessary for a better-sustained life, any disorder can not only affect the mobility but also may result in many functional abnormalities. The rheumatologists, orthopaedists and neurologists are the ones who treat the conditions that affect the muscles. Following are the diseases caused due to the
-
muscles: Muscular dystrophy: It affects the muscle fibres and its symptoms are weakness, loss of mobility and lack of coordination.
-
Cerebral Palsy: It refers to the posture, balance and motor functions. The extreme effect may result in brain disorder and is one of the common congenital disorders.
-
Myasthenia gravis: As it is a chronic autoimmune disease, it results in muscle weakness and fatigue. It also results in difficulty in breathing and swallowing.
-
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): Often referred as Lou Gehrig’s disease, it is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects the nerve cells of the brain.
G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.