
What is the first thing that comes to your mind when you think about the Skeletal System? The Bones. Did you know that your height depends on the growth of your bones? Bones form the integral part of the Skeletal System. The human Skeletal System, also called as, the internal skeleton, consists of many bones and cartilages and subdivides the system into two parts, namely, the axial part and the appendicular part. About 15-20 percent of the total body weight is made up by the skeleton.
Bones provide the shape to the body. They provide a rigid support to the body and hence are the primary organs of the Skeletal System. Strong and light, bones are the moist living organs that permit easy movement. It also protects the delicate organs like the heart, brain, etc. The Skeletal System acts as a network of the tendons, ligaments and cartilage. The important functions of Skeletal System include support, movement, protection, blood cell production, calcium storage and endocrine regulation.
The two distinctive parts of the Skeletal System are:
-
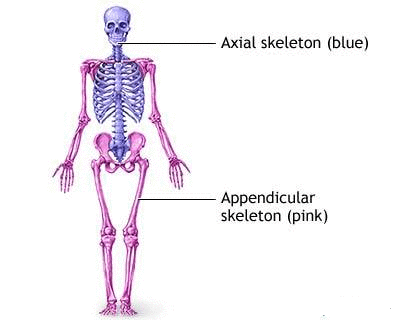
Axial Skeleton: It involves the vertebral column, the rib cage and the skull. It helps the humans to maintain the upright posture by transmitting the weight from the head, the trunk and the upper extremities to the lower extremities at the hip joints.
-
Appendicular Skeleton: With a total of 206 bones, it is formed by the pectoral girdles, the upper limbs, the pelvic girdle and the lower limbs. It is mainly responsible for walking, running and other movements and protecting the major organs that perform digestion, excretion and reproduction.
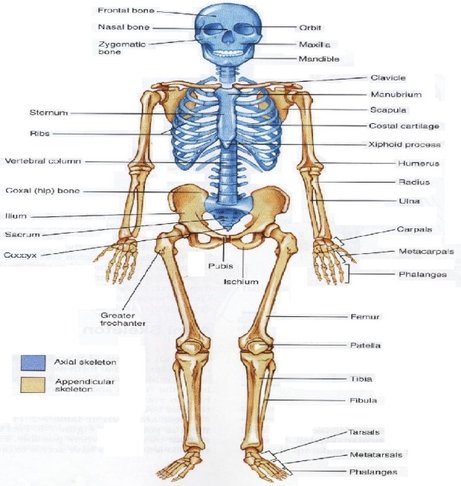
As bones come in many shapes and sizes, some are solid with a spongy bone on the inside whereas others are filled with juicy jelly-like red marrow. They are classified as long, short, flat and irregular ones. The important bones include:
-
Skull: it helps in protecting the brain
-
Shoulder blade: It is also medically known as Scapula. It is the bone that connects the upper arm bone to the collar bone.
-
Ulna: One of the two long bones in the forearm and also called the elbow bone, it is located at its side and to the side of the little finger
-
Radius: It is the second long bone in the lower arm, but is comparatively shorter than Ulna
-
Upper arm bone: Known as Humerus, it is a funny long bone or forelimb that links the shoulder to the lower arm or the elbow
-
Sternum: Also called as the breastbone, it is a flat bone that is attached to the mid-front of the rib cage
-
Ribs: Ribs surround the chest to enable and facilitate breathing and protect the lungs, heart and other internal organs of the thorax
-
Pelvic: It supports the organs in the abdomen and anchors the legs and is also known as the hip or gridle
-
Thigh bone: The largest bone of the body, the femur, connects the hip to the knees and facilitates walking, jumping, running etc.
-
Shin bone: It is known as the Tibia and it connects the knee to the foot.
-
Fibula: It is also known as calf bone and is located to the lateral side of the tibia, above and below.
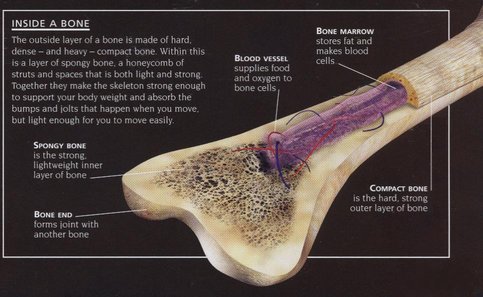
Structurally, the bone has six main parts:
-
Diaphsys: It is a rigid and a strong structure that is light in weight to permit easy movement. It is a hollow tube made up of cortical bone and it usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue.
-
Medullary cavity: It is an inactive and fatty form of marrow which is found in the adult skeleton. Also the hollow area inside the bone contains a soft and yellow bone marrow.
-
Epiphyses: It fills in the small spaces of the spongy bone and is a red bone marrow.
-
Articular cartilage: Covering each epiphysis, it is a thin layer that acts like a small rubber cushion
-
Perosteum: It is a strong fibrous membrane that not only covers the joint surfaces but also a long bone
-
Endosteum: It lines the medullary cavity of the long bones. Its surface is absorbed in the periods of malnutrition that leads to less cortical thickness.
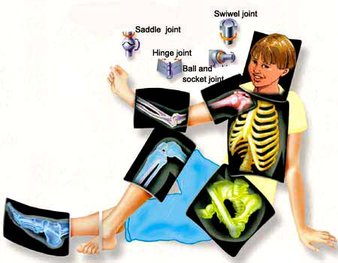
Joints connect two bones together. There are about 200 types of joints in the body. The main ones include:
-
Ball and Socket Joint: Also called as spheroidal joint, it is a joint where the ball-shaped surface fits into the cup-like depression of the other bone.
-
Ellipsoidal Joint: They are responsible for the movements of the joints in the knuckles and the toes. It gets formed when the oval end of one bone fits into the oval cup-shaped end of another bone.
-
Hinge Joint: As the name suggests, it acts like a hinge that allows the bending and the straightening of the joints. They are usually found in the knee, ankle and elbow.
-
Pivot Joint: It swivels in a collar formed by the other and allows the head to turn.
-
Plane Joint: It is also known as gliding joint. They are flat and allow limiting sliding movements and are found between the ankle bones in the foot and the wrist bones in the hand.
-
Saddle Joint: It is found at the base of the thumb where the two U-shaped bone ends meet. It allows the rotation in two directions.
The diseases are:
-
Osteoporosis: One of the common diseases of the Skeletal System, it is particularly seen among the adults. It causes the bone to lose calcium, become thinner or disappear completely and leads to the loss of the bone tissue.
-
Scoliosis: Often pronounced as ‘C’ or ‘S’, it is a side-to-side curve in the back or the spine. The symptoms are seen during adolescence.
-
Arthritis: It is an inflammatory disease that damages the joints and their structures. It attacks joints, joint capsules, the tissues, etc. and affects the joints of the neck, shoulders, hands, lower back, hips or knees.
-
Leukemia: It is a cancer that starts in the marrow of the bone and affects the blood. It allows the abnormal white blood cells to multiply uncontrollably and affects the production of normal white blood cells and red blood cells.
-
Bone Cancer: Bone Cancer originates in the bones and spreads to the other parts of the body.
-
Bursitis: Refers to the pain in the joints caused by this disorder. It generally affects the shoulders and the hip joints. Bursa is the small fluid-filled bags which act as a lubricating surface for the muscles to move over bones. When the bursa is inflamed, Bursitis is caused.
G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.