
We are all under the general impression that the brain is the most important and vital part of the human body. It helps us to understand, think and perform accordingly. However, deep inside the system of the body, there are bundles of nerves that run down the middle of the backbone which actually work independent of the brain. These nerves send responses to the muscles directly. It is the Spinal Cord. It acts as a channel link between the brain and the other parts of the body. However the Spinal Cord stops growing after five years of age.
Spinal Cord is a long and thin tube that bundles the nervous tissue and the support cells that runs down from the base of the brain, that is, the medulla oblongata. The Central Nervous System is together made up by the brain and the Spinal Cord. Beginning at the occipital bone, the Spinal Cord extends to the space between the lumbar vertebrate, though does not extend the entire length of the vertebral column. It is about 18 inches long and is as thick as the man’s little finger. Also, the spinal fluid protects the cord from damage.
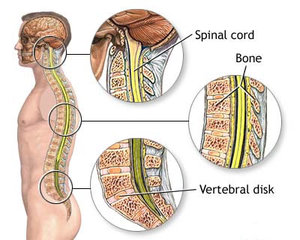
The extension of the Spinal Cord is comparatively shorter than the bony spinal column. The human Spinal Cord terminates in a fibrous extension known as the filum terminale from the foramen magnum through the conus medullaris. The segments of the Spinal Cord play an important role in the functioning of the body. It is at the C3 to T2 segments that the sensory input comes and motor output goes to the arms. The location between the L1 to S3 segments looks after the sensory input and motor output from and to the legs. The three layers that protect the Spinal Cord are the spinal meninges, the dura mater and the arachnoid mater. The space between the dura mater and and the bone of the vertebrae is called the epidural space and that between the arachnoid and the pia meter is called the subarachnoid space. The peripheral region of the cord contains neuronal white matter in the cross section. The central region of the peripheral region is made up of the nerve cell bodies and surrounds the central canal known as the ventricles.
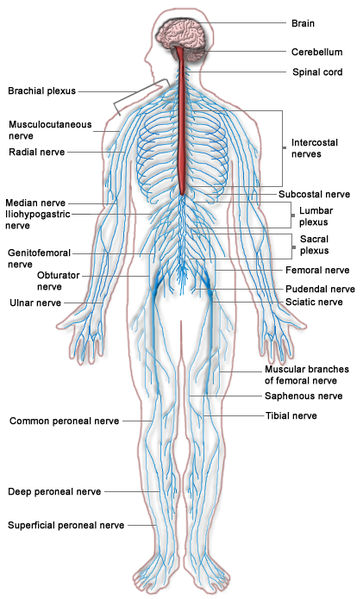
The Spinal Cord is divided into 31 segments. The right and the left pairs of the spinal nerves are formed at every segment. The nerve roots are formed with a combination of the nerve rootlets. Also the combination of the ventral and the dorsal roots form spinal nerves on each side of the Spinal Cord. The segments are classified as:
-
8 cervical segments that forms 8 pairs of cervical nerves
-
12 chest segments that forms 12 pairs of the chest nerves
-
5 lumbar segments that forms 5 pairs of the lumbar nerves
-
5 sacral segments that forms 5 pairs of sacral nerves
-
3 coccygeal segments that join together to form a single pair of coccygeal nerves
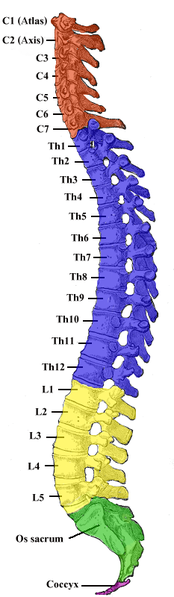
The vertebral segments correspond with the Spinal Cord segments in the fetus. The two regions of the Spinal Cord enlargement are:
-
Cervical enlargement: It includes the segments from about C4 to T1
-
Lumbosacral enlargement: It is composed of the segments L2 to S3 and is also found in the vertebral levels of T9 to T12
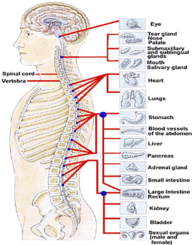
Generally, the Spinal Cord is considered as ‘the information highway of the body’ because it is due to the Spinal Cord that we perform reflex actions, especially at the time of an emergency, the Spinal Cord gets the signals so that the lapse decreases. It is because of the Spinal Cord in the human body that an individual stands straight and is able to sleep on their backs. Also the Spinal Cord is responsible for transmitting messages of pain, movement, temperature, touch and vibration of the skin, joints, muscles and other internal organs. In addition to this, there are three important functions that the brain and the Spinal Cord perform in harmony:
-
Motor Functions: It directs the voluntary muscle movements
-
Sensory Functions: These are responsible for monitoring the sensation of touch, pressure, temperature and pain
-
Autonomic Functions: They regulate digestion, urination, body temperature, heart rate and the contraction of the blood vessels
The Spinal Cord injury is a result of damage to the cells in the Spinal Cord that causes a loss of communication between the brain and the other parts of the body. The higher the injury, the greater the problems associated with the injury. Spinal cord injuries are classified into the following:
Complete Spinal Cord Injury: It is the loss of sensation and motor ability caused by bruising, loss of supply of blood to the Spinal Cord, pressure on the Spinal Cord. They result in total loss of sensation and movement below the site of the injury.
Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury: Though they do not result in complete loss of movement, there are variety of patterns:
-
Anterior Cord Syndrome: It is caused due to the damage to the motor and sensory pathways in the anterior areas. This results in loss of movement and overall sensation.
-
Central Cord Syndrome: It is caused due to the injury of the cervical area of the cord and affects the corticospinal tract that is responsible for carrying signals between the brain and the Spinal Cord.
-
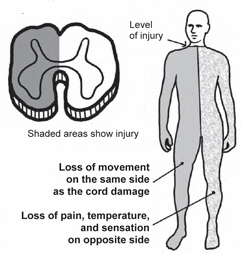
Brown-Sequard Syndrome: It is a result of the injury to the right or left side of the Spinal Cord. Its effect is loss of sensation of the temperature.
-
Injuries to the individual nerve cells: It results in loss of sensory and motor function and hence the symptoms vary according to the location and the function of the nerve root.
-
Spinal Contusions: This is a very common type of Spinal Cord injury. Its consequences are inflammation and bleeding from the blood vessels near the injury.
G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.