
Swaziland or officially known as the kingdom of Swaziland is a landlocked country situated in Southern part of Africa. It shares its borders with South Africa to the west, north and south, and with Mozambique to the east. Swaziland derived its name after the 19th century king Mswati II. Lobamba is the legislative capital of Swaziland and Mbabane is the administrative capital and the largest city of Swaziland. The highest point in the country is Emlembe at 1862 m and the lowest at Usuthu River at 21 m. Swaziland comprises of mostly mountainous and hilly areas with moderately sloping plains.

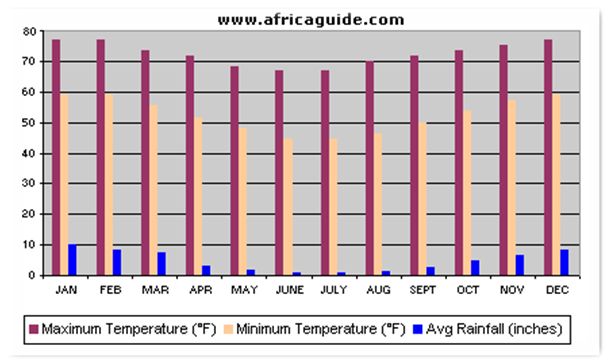
The climatic conditions in Swaziland vary from tropical to temperate. Swaziland has four seasons in a year; Spring (September to October), Summer (November to March), Autumn (April to May) and Winter (June to August). The seasons in Swaziland are completely reverse to that of the countries situated in the Northern Hemisphere – December being the Summer and June being the Winter. The regions in the higher altitude are much cooler and cloudy than the other regions of the country. The Western part of the country that includes the mountains, faces high level of humidity. These mountainous regions receive high rainfalls, which are accompanied by thunderstorms. Rainfall in the country is mostly experienced during the summer months. The temperatures and rainfall in the eastern parts is comparatively less than the central as it experiences much drier climate. The important factor that affects the weather conditions in Swaziland is the maritime air, originating in the Indian Ocean.
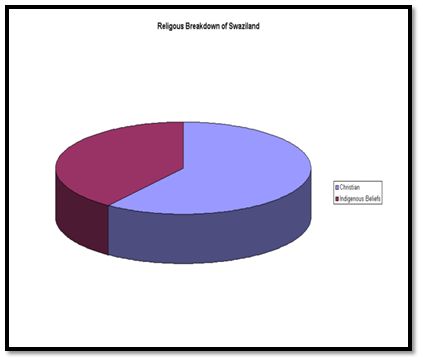
The constitution of Swaziland allows freedom of worship for all the religions. Majority of the population consists of followers of Christianity with about 40% of the population comprising of Zionists (blend of Christians and indigenous ancestral worship). About 20% of the population consists of Roman Catholics with other Christian denominations like Anglicans, Methodists and Mormons that account for another 20% of the population. A small number of non-Christian groups, comprises of followers of Islam that account to 10% of the population. There are small groups of Jews and Baha’is that account to another 10% of the population. These small groups are generally located in the urban developed areas.
English and Swazi are the official languages of Swaziland. Swazi, a southern Bantu language, is also the national language of the country. Swazi is spoken by about 95% of the Swazi population. The proceedings of the parliament take place in both English and Swazi. Swazi language teaching is present in all the national schools. English is the medium of instruction in all the state and private schools and institutions. A small minority of the people speak Zulu and a few smaller groups speak Tonga. Afrikaans is also spoken by the people of Afrikaner descent.
Swazi houses are traditionally like beehive huts that are made using dry grass. In the Polygamous families, every wife has their own huts and yards that are surrounded by reed fences. Basically there are three structures: for sleeping, cooking and storage respectively. In the larger households, there is additional structure for guest accommodations. To the centre of the huts there is cattle byre, a circular area enclosed with large logs. The cattle byre has ritual and practical importance as storage of wealth and symbol of prestige. The sangoma is the traditional healer, which is usually selected by the ancestors of the particular family. The training of these healers is called ‘Kwetfwasa’. The healer is consulted by the people for the reason of death and sickness. Their treatment is based on ‘kubhula’, a procedure of communication, through trance, with natural super powers. The most important cultural event is Incwala ceremony, which is held in December or January depending upon the phases of the moon. Incwala in English is often known as ‘first fruits ceremony’. Without the presence of the king this event is not celebrated and it is considered a high treason for any other person to hold an Incwala. Among the most popular cultural fests is the annual Umhlanga Reed Dance, an eight-day fest in which girls cut reeds and present them to the queen mother, followed by the traditional dance. Only childless and unmarried girls are allowed to take part in this traditional festival. The royal family also appoints a captain among the girl whose duty is to announce on the radio about the event dates and one of the King’s daughters is her counterpart during the event. The basic aim of this event is to provide tribute labor for the Queen mother. The people of Swaziland are also known for a strong presence of their work in the handicrafts industry. The products made are unique and they reflect the culture of Swaziland that range from house wares, to artistic decorations, to complex glass, stone or wood artwork.
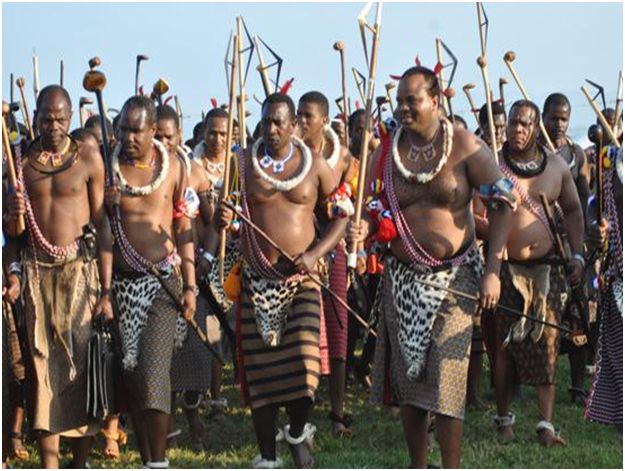

Incwala ceremony
G Kowledge of | 0 Comments >>
0 Comments
Leave Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked.