
Do you know which is the most complex organ in the human body? Or have you ever realised how are you able to pay attention to what you are reading now? All this seems mysterious and confusing, isn’t it? For instance, how do you understand that you are hungry and you want to eat, or how and why do you cry? From our thinking to our behaviour, from our behaviour to our perception, from our perception to our response and from our response to our reaction to a particular situation… everything that we do is because of our Brain. Without our Brain our body will not function. Our Brain is the most complex organ in our body, it has the capacity to store in more information than all the libraries in the entire world put together. Like the term ‘Brain dead’, if the Brain does not function, the person is considered dead.
The Brain is the most complex and the most important organ in our body that is the centre of the nervous system. The Brain is situated in the head, close to our sensory organs for vision, balance, taste, hearing and smell.
The human Brain weighs about 3 pounds and is the most complex organ, which is made up of billions of cells that continuously interact and work at a lightning speed.
The human Brain consists of three main parts:
-
Cerebrum
-
Cerebellum
-
Brain stem
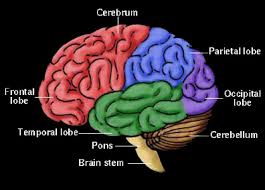
The largest part of the Brain that is associated with the conscious thought, sensation and movement is the cerebrum. The cerebrum is divided into two halves: the left and the right hemispheres. Both the hemispheres appear like mirror images of each other, though they are different. The movements of the left side of the body are controlled by the right hemisphere, whereas the movement of the right side of the body is controlled by the left hemisphere.
-
Left Hemisphere: The left hemisphere basically controls and regulates the language, speech, the hand movements and other right side body movements.
-
Right Hemisphere: The right hemisphere controls the left-sided body movements.
The cerebrum is made up if four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal and the occipital lobes.
-
Frontal Lobe: The frontal lobe is situated right under the forehead. The frontal lobe is among the four lobes of the cerebral hemisphere. The main function of the frontal lobe is that it controls attention, behaviour, creative thought, problem solving, smell, physical reaction, emotion, coordinate movements and our personality.
-
Parietal lobe: The parietal lobe is one of the four lobes of the cerebral hemisphere that is situated near the back and on top of the head above the ears. The parietal lobe controls our ability to write, read, and understand relationships.
(|)Sensory cortex is situated in front of the parietal lobe and its main function is to receive information from the spinal cord like pressure, pain, sense of touch and the position and movement of the body parts.
(||)Motor Cortex is an area situated in the top middle part of the Brain, which helps in controlling the movements of various parts of the body. -
Temporal lobe: The temporal lobe is one of the four lobes of the cerebral hemisphere that is situated at the side of the head above the ears and also behind and below our frontal lobes. The key function of the temporal lobe is to control auditory and visual memories, along with controlling language, behaviour and some hearing and speech.
(|)Wernicke’s area is the part of the temporal lobe which basically surrounds the auditory cortex and is essential for formulating and understanding speech. Deficits in this particular area can lead to difficulty in understanding the spoken language. -
Occipital lobe: The occipital lobe is one of the four lobes of the cerebral hemisphere that is situated in the back of the head and its basic function is to control sight.
The Brain stem is the lower part of our Brain that starts from the Brain and ends at the spinal cord. The Brain stem consists of nerve fibers, which carry the signals to and from all parts of the body. The Brain stem has many vital functions which include sensory and motor pathway, respiratory and cardiac functions and reflexes of the body. The Brain stem includes the pons and the medulla.
Pons: The pons consists of many control areas of the eyes and the face movements.
Medulla: The medulla is situated in the lowest part of the Brainstem and it is the most important part of the Brain as it contains the critical control centres for the lungs and the heart.
The cerebellum is situated at the lower back of the head and it is connected to the Brain stem. The cerebellum controls and regulates all the motor functions like walking, posture, balance and our general motor coordination.
The hypothalamus is a region of the Brain that works with the pituitary gland to control the hormonal process of the body as well as the temperature, hunger, thirst and mood.
The pituitary gland is a small, bean-sized organ that is situated at the base of the Brain and is also connected to the hypothalamus. This gland is important as it secretes essential hormones for sexual and growth maturation.
The thalamus is situated near the centre of the Brain. The thalamus regulates input and output to and from the Brain, and it also controls the sensation of attention and pain.


