
What is the first thing that comes to your mind when you think about the word ‘Cardiovascular’? It is the ‘thumping’ of the heartbeat, isn’t it? The Cardiovascular System is powered with a hard working organ – the ‘heart’. This is because the heart pumps blood throughout the body even when it is at rest. The sound of the heartbeat is made by the closing of the four valves of the heart.
The Cardiovascular System transports the nutrients and removes the gaseous waste from the body. It comprises the heart, blood vessels and blood.
-
Heart: Just the size of the fist, the heart is responsible for the supply of blood and oxygen to all the parts of the body. The heart contracts and relaxes in a coordinated manner or in a rhythm and this rhythm is what is known as heartbeat. The impulses that produce these beats are carried out through the process called cardiac conduction.
-
Blood Vessels: They are a network of hollow tubes, which transport blood throughout the body. The blood travels from the heart to smaller arterioles through the arteries, later moves to the capillaries, venules, then to the veins and back to the heart. Arteries, veins, capillaries and sinusoids are types of blood vessels. The blood exchanges the nutrients and substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide and other wastes with the fluids that surround the cells. This process is called microcirculation.
-
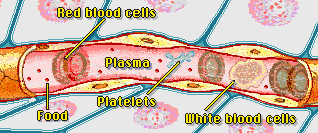
Blood: The main function of the blood is to deliver the nutrients to the cells and remove the wastes during the process of cell respiration. It is composed of Red Blood cells (RBC) and White Blood cells (WBC), platelets and plasma. The protein that the Red Blood contains is haemoglobin. It is responsible for binding the oxygen as the oxygen molecules enter and transport them to various parts of the body. Blood cells, carbon dioxide, glucose, hormones and proteins are the important elements of blood. Carbon dioxide plays a major role in cellular or aerobic respiration by delivering blood to the tissues in the body and resulting into the break down of nutrients like sugar and fats for energy.
Blood Cells are of four types:
-
Red Blood Cells: Also known as RBCs or erythrocytes, they are the most abundant cells in the body and they contain haemoglobin. They are generally slightly intended and flattened disks. At the end of every four months, each RBC gets degraded by the spleen and the Kupffer cells in the liver.
-
Haemoglobin: It is a protein, which contains iron and transports oxygen from the lungs to the body tissues and the cells.
-
White Blood Cells: Also known as Leukocytes, they defend the body against infections and are the cells of the immune system. Lymphocytes and granulocytes are the two types of WBCs. WBC fights the abnormal cells and prevents the body from cancer. In a healthy individual, the WBCs make up to about 1 percent of the blood.
-
Platelets: Platelets are also known as thrombocytes. They prevent the body from blood clotting. If exposed to air, platelets break down and release fibrinogen into the bloodstream.
Cardiovascular System is significant for the body as it performs three important roles:
-
Transportation: It becomes one of the important responsibilities of the Cardiovascular System to transport blood to the body tissues. The blood then transports the hormones throughout the body by the blood’s liquid plasma.
-
Protection: The system protects the WBCs that helps in cleaning the cellular debris and fight the pathogens of the body. On the other hand, the platelets and the RBCs seal wounds and prevent the body liquids from leaking out.
-
Regulation: The blood vessels regulate the body temperature and control the flow of blood to the surface of the skin. The hot blood in the body, dumps its heat to the body’s surroundings because the blood vessels open during times of overheating, especially near the skin surface. Also, blood helps to maintain the pH balance of the body because of the presence of carbonic acid – bicarbonate buffer thereby maintaining an isotonic environment.

When you inhale, blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs. The oxygen in the air gets mixed with it when we breathe. From the lungs, this oxygen-rich blood travels to the heart and gets pumped through the arteries and the capillaries. It delivers oxygen to all the tissues and cells of the bone, along with bones and skin. Later, the veins carry the oxygen-depleted blood to the heart for another circle. In this manner, the breathing continues and oxygen is transported to various parts of the body.
The most common diseases caused due to the heart are:
-
Heart Attack: It is a result of lack of blood in the body. This lack of blood happens due to a clot that is developed in one of the heart vessels. The supply of blood stops, if the clot gets big enough. Vomiting, nausea, dizzyness, difficulty in breathing and appearance of the face as grey are the symptoms of heart attack. Also, the constant chest pain that shall not calm down regardless of sitting or lying down is another important symptom.
-
Heart Cancer: It is very rare and causes tumours in the heart. To the adults it is caused in the upper right heart chamber. It happens when the cells around the blood vessels become cancerous. The first common heart cancer is known as angiosarcoma and the second common one among the children is called rhabdomyosarcoma. It begins from the cancerous muscle cells. The common symptoms of heart cancer are chest pain, irregular heart rhythms, breath shortness and fatigue.
-
Atherosclerosis: It is the hardening and narrowing of the arteries. It begins with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, that damages the endothelium or smoking cigarettes etc.. The first symptom is a heart attack.
-
Angina: It is one of the serious causes of chest pain. Its common symptoms include chest pain or discomfort, pain in arms, neck, jaw, or shoulder, nausea, fatigue, shortness of breath, sweating and dizziness.
The detoxification of the blood is required when an individual has skin problems, aches and pains, or indigestion. It rests, cleans and nourishes the body within and from the outside. It is required to remove the impurities from the liver, kidneys, intestines, lungs, lymph and skin. It performs this cleaning function through the following process:
-
It rests the organs through fasting
-
Stimulates the liver to drive toxins from the body
-
Promotes the elimination through kidneys and intestines
-
Improving the circulation of blood
-
Refuelling the body with healthy nutrients
Few ways that keep your heart healthy are:
-
Eat Healthy
-
Maintain healthy body weight
-
Practice yoga, meditate or exercise
-
Be active
-
Quit smoking and alcohol
-
Manage stress levels
-
Check your family history
-
Get good sleep
-
Get regular health screening
-
Laugh out loud and be happy


