
Music is a link that connects the past to the present and musical instrument is a thread that joins different cultures. The Cello is one such continuous instrument having a glorious past as well as a dynamic present. It is basically a bass instrument with low frequency or range. It lends harmonic or rhythmic support to the orchestra and is the lowest part of the harmony. It is a string instrument of the violin family, and is basically a tenor and bass instrument and is described as the closest sounding instrument to the human voice. Mostly associated with the Baroque Era of European classical and instrumental music, the Cello was a part of the standard orchestra and the bass voice of string quartet and chamber music. The Baroque Era was a period of artistic style that used exaggerated movements and interpretation to produce drama and music and is referred to as the ‘Golden Period’ when music was being re–invented. The main ensemble of musical instruments of the Baroque era was the unfretted, bowed strings instruments of violin family and the most important being an instrument in the approximate range of a Cello. A number of concerts and sonatas have been written for the Cello. Let us learn more about this instrument.
A Cello from the violin family has been developed from the viola during the 15th century in upper Italy. However, between 16th and the 17th centuries, the term ‘bass instrument’ was used to describe the gamba and violin family. Later, it was used only for the violin family. The term ‘violoncello’ was first used by some Italian composers. Also called as the violincino, the violin Cello or ‘Cello’ became the most commonly used term for the instrument. Renowned violin makers Andrea Amati (1581–1632), Gasparo da Salo (1549–1609) and Paolo Maggini (1581–1632) were the first to make Cellos and new standards were set by Antonio Stradivari (1644–1737).

A Cello is held upright between the legs with the tail–pin resting on the ground, which is a very stable position. The sound of the Cello is produced by either moving the bow over the strings or plucking it with the right hand. With the help of the finger tips of the left hand, the pitch alterations are achieved by pressing down the string on the finger board. This raises the pitch by shortening the vibrations. The fingering is chromatic where each finger plays a semi tone with the first and second finger playing the entire notes. The bow is held at the frog at right angles by four fingers to produce pure notes.

The components of a Cello are scroll, tuning pegs, finger board, bridge, tailpiece, endpin, saddle, fine tuners, F holes, nut and the stick.
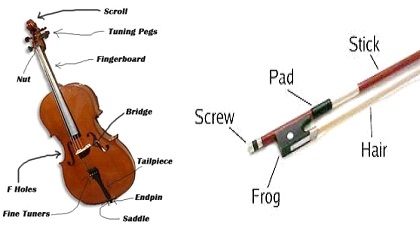
The machine–made Cello is made from laminated wood, carbon fibre or aluminium whereas the traditional Cello is made from spruce, maple, poplar and willow. The traditional Cello has a spruce top and maple back and sides. The sides or ribs are made from wood, which is heated and bounded onto various ‘forms’ and shapes’ .The Cello has a wide top and bottom bout and a narrow middle. This narrow middle is formed by two C–shaped bouts and the bridges and F–holes are placed below the middle part. A decorative inlay border called purfling adorns the top and back of a cello. The purfling adds to the beauty as well as prevents cracking of the wood. The neck, pegbox and scroll are made from one single piece of maple wood and the fingerboard is glued to the neck. The Cello strings are traditionally made from gut (sheep or goat) but modern strings are made from metal. The bridge holds the strings; the F–holes are placed on either side of the bridge and are a part of sound production. The bass bar (placed inside) and the sound post placed between the two plates of the Cello transfer the vibrations. The tail–piece and the endpin fitted at the lower end prevent the Cello from slipping on the floor. The Cello is played with a curved bow.

Hard rock and metal are usually the sub–genres of rock music characterized by the use of Cello. Often used in the groups of three or more instruments, Cellos are used to create music of unique timbre and texture of different rock music including instrumental rock, jazz rock, rock and roll and Sufi rock.

Cellos can be differentiated from their size and make. There are French Cellos, Italian Cellos, German Cellos as well as Chinese Cellos. Sizes, however, varies from larger than average full size Montagnana Cellos or a smaller Suzuki cellos. Cellos are handmade as well as machine made and electronic Cellos also are available.

Some of the legendary (deceased) cellists include J.S Bach, Haydn, Pablo Casals, Giovanni Battista Cirri and Muhal Richard Abrams. Saskia Rao de Haas and Amit Peled are the contemporary Cello players.
Oxford Cello School of UK and Mansfield Public Schools for Violin/Cello in USA are well known schools. Cello is a bowed stringed instrument and is also called as violoncello. It is played as a violin. To be a good Cellist, one has to be focussed and follow these steps:
- Take a decision to learn to play the Cello.
- Be dedicated.
- Get a good teacher.
- Learn the basics.
- Include daily practice in the schedule.
- Increase the duration of practice session gradually.
- Observing and joining a music group.
There are teachers available to teach who are established as players. Beginners may learn to play in 8 weeks, few months, a year or more than a year. However, there are other music schools in UK, USA, Germany, Japan and other countries.


