There is always something that we never forget despite the busy schedule and life’s hurdles. And that is breathing. If we did not breathe, we couldn’t live. Generally even at rest, we breathe about 12-15 times a minute. Also, why do we yawn, sneeze and get hiccups? It is the Respiratory System which is responsible for this. Breathing is the most important function of the system and breathing in and out, constitutes the respiratory cycle.
The Respiratory System comprises of a series of organs that are responsible for taking in oxygen and giving out carbon dioxide. It is also known as the Ventilatory System. It is a system that biologically brings the gases inside the body and leads to gas exchange. The Respiratory System includes airways, lungs and the respiratory muscles. The exchange process that takes place in the alveolar region of the lungs enables the molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide to be passively exchanged through diffusion between the gaseous external environment and the blood.
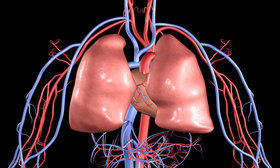
Important parts of the Respiratory System are:
-
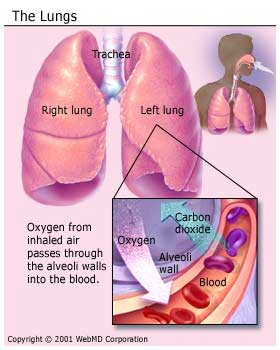
Lungs: The lungs are responsible for taking the oxygen into the body when we breathe in. The red blood cells then pick out the oxygen in the lungs and carry the oxygen to all the parts of the body that requires it, for optimal functioning. The red blood cells then transport the carbon dioxide back to the lungs which is sent out from the body when we exhale.
-
Trachea: Also known as windpipe, it filters the air that we breathe in and moves it to the bronchi.
-
Bronchi: They are the two air tubes which are responsible for carrying air directly into the lungs through the trachea.
-
Diaphragm: It is located at the bottom of the lungs. It is because of the diaphragm that the breathing begins. The diaphragm contracts and pulls downward when we breathe in and this helps in enlarging the space of the lungs. The larger the space, the more the air that can be pulled in. it is usually the main muscle in breathing.
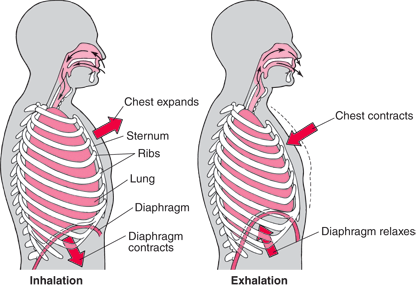
The primary role of the Respiratory System, as the name suggests, is respiration. This involves the absorption of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide. This process is carried out through the cycle of inhalation and exhalation. Both of these gases perform different functions. Oxygen helps the other organs in the body to survive whereas carbon dioxide helps in releasing the waste products from the body. The parts of the Respiratory System, divided into the upper tract and the lower tract, perform various functions. The upper tract that includes the nose, throat, voice box and trachea acts as a passageway for oxygen and carbon dioxide during breathing; whereas the lower tract that comprises of lungs, bronchi and alveolar sacs helps in the process of exchange of gases. Also the Central Nervous System, the diaphragm, the lungs and the Circulatory System control the process of breathing. Muscles in the lungs and the ribs help in the expansion and contraction of the lungs when we breathe. This process helps the oxygenated blood to enter the Circulatory System and reach the other parts of the body.
The diseases are:
-
Asthma: It is caused when the bronchi and the bronchioles are inflamed. This leads to difficulty in breathing and causes restriction in the airflow into the alveoli. The common things that trigger asthma are air pollution, tobacco smoke, factory fumes, cleaning solvents, infections, pollens, foods, cold air, exercise and other chemicals.
-
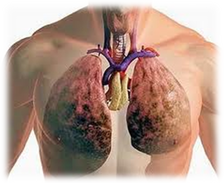
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: It leads to difficulty in breathing. It is a combination of three conditions, namely, chronic bronchitis, chronic asthma and emphysema
-
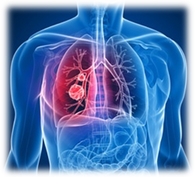
Lung Cancer: Active and passive smokers are prone to lung cancer. It is caused by the growth of certain abnormal cells in and around the lungs
-
Bronchitis: In this condition, mucus is produced when the membranes that line the larger bronchial tubes are inflamed. The common symptom is bad cough.
-
Common Cold: It is one of the 200 viruses of the problems in the Respiratory System. The common symptoms are mild fever, cough, headache, sneezing and sore throat.
-
Cystic Fibrosis: It is a hereditary disease that affects the lungs because abnormal thick and sticky mucus blocks the airways in the lungs and develops bacteria into it. It is an incurable disease.