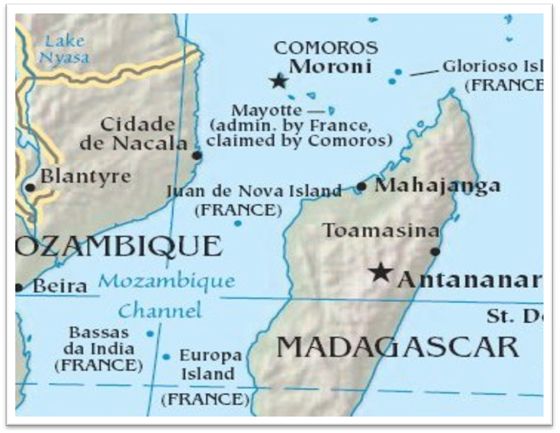
Juan de Navo Islands, officially Saint Christophe, is a French possession in Reunion by a high commissioner. The land only has a French garrison and a weather station. Guano deposits are in abundance on the Juan de Nova. It is named after the Spanish Explorer in the 15th century and is in possession of the French since 1897. However, due to its location, it is also claimed by Madagascar.
Juan de Nova island is located in the narrowest part of the Mozambique Channel and is about a way between the Madagascar and the Mozambique Channel. The island is administered by the French Southern and Antarctic Lands. It is claimed by the Madagascar as it lies within its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of about 61,050 sq. km. The island lies between the geographic coordinates of 17°03’S latitude and 42°45’E longitude. Comparatively, the island is seven times the size of the Mall in the United States. Stretching a coastline of 24.1 km, Juan de Nova covers a total area of 4.4 sq. km. The natural resources are fish, crayfish, phosphate and guano.
A Spanish explorer, who was in the service of the Portugal discovered the island in 1501. The name of the island was after his name, Juan de Nova. However, the French possessed the land in 1897. Once the land was discovered, it was heavily exploited for the Guano and Phosphate from the start of the 20th century. However, the French abandoned the land during the World War II.
Juan de Nova enjoys a tropical climate. Due to its location, at the narrowest part of the Mozambique Channel, the land is low, flat and sandy. However, almost 90% of the land is a forest, as there are no inhabitants in the island. The land has a wildlife sanctuary and is surrounded by the seabirds and the sea turtles.



