Manganese is a trace mineral which is required in very less quantity but its deficiency or toxicity might cause serious physical and mental problems. Let’s see how important it is for our body.
Manganese is required in the formation of connective tissues and bones. It also helps blood clotting and formation of sex hormones. It helps in various other body mechanisms such as metabolism of fat, carbohydrate, protein and nucleic acid; calcium absorption and the regulation of blood sugar level. It is an important component of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase, which help in neutralizing the free radicals and prevent cell damage. Manganese is an essential mineral for the pancreatic, brain and nerve functions.
The daily requirement of Manganese is based on the age group and sex. Infants need to have a daily intake of 0.003 to 0.6 milligrams per day while children should have a daily dosage of 1.2 to 1.9 milligrams. Adult males need more Manganese than females. 2.3 milligrams per day should be consumed by an adult male per day while a female should have 1.8 milligrams as daily intake. Amongst the women, the intake differs as per the situation. Pregnant women need 2 milligrams of Manganese per day while a breast feeding mother should have a daily intake of 2.6 milligrams on a daily basis.
The animal food sources of Manganese are oyster, fish, turkey, chicken and liver and kidney of the meats. Among the plant foods, the Manganese sources are wheat germs, legumes, nuts, rolled oats, soybeans, pulses, rice, corn, potatoes etc.
Deficiency of Manganese leads to infertility, reduced glucose and protein metabolism. It also causes malformation of the bones, and weakens the tendons and ligaments which lead to a disease known as myasthenia gravis where the muscle loses it strength. It also causes a neurological disease known as ataxia which is actually due to the lack of muscle contraction, eventually affecting ones abilities to speak, eye movements, walking and other physical movements.
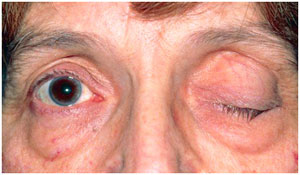
Myasthenia Gravis
The side effect of consumption of Manganese in excess is anaemia because Manganese interferes in the absorption of iron. Some of the other symptoms of Manganese overload are psychiatric illness, mental confusion, impaired memory, loss of appetite and spastic gait (abnormality in walking where the legs are held closer than normal). The excess Manganese might also lead to abnormal concentration in the brain leading to neurological disorders.
The first major cause of Manganese deficiency would be intake of food with less Manganese. Another factor is excessive sweating, people who go through such condition due to their occupation or any other disorder might face the problem of Manganese deficiency. Other causes could be the excess consumption of iron, calcium and phosphorus; because these minerals can deplete the Manganese in our body within a short period of time.


